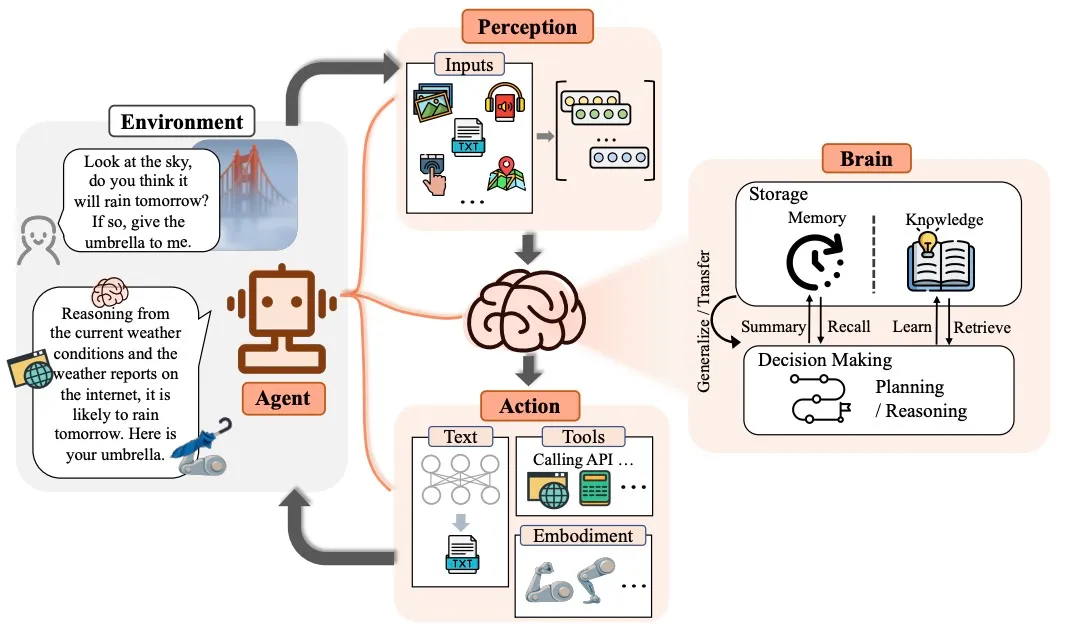
At their core, AI agents are intelligent, autonomous systems designed to complete tasks with minimal human intervention. They differ significantly from standard AI assistants and chatbots by being capable of handling complex, multi-step workflows.
AI agents are typically components of larger AI systems rather than standalone applications. They are powered by large language models (LLMs) and have access to external tools, APIs, and databases to execute various tasks. Think of AI agents as specialized workers within an AI-driven ecosystem. For example, a customer support AI system might consist of multiple agentic flows, each handling different aspects of a user inquiry:
- A Query Classification Agent determines the nature of the user's issue (billing, technical support, or general inquiry).
- A Knowledge Retrieval Agent fetches relevant documentation or previous cases to provide useful responses.
- A Ticket Management Agent decides whether the issue can be resolved automatically or needs human intervention.
- A Follow-up Agent ensures that unresolved issues are tracked and followed up on in a timely manner.
Each agent specializes in a particular function but works together as part of a cohesive system, ensuring efficient and accurate task completion.
Think of a chatbot as an espresso machine—it can brew coffee when prompted. Meanwhile, an AI agent is like a skilled barista who not only brews coffee but also takes orders, serves customers, handles payments, cleans up afterward, and even restocks supplies when needed.